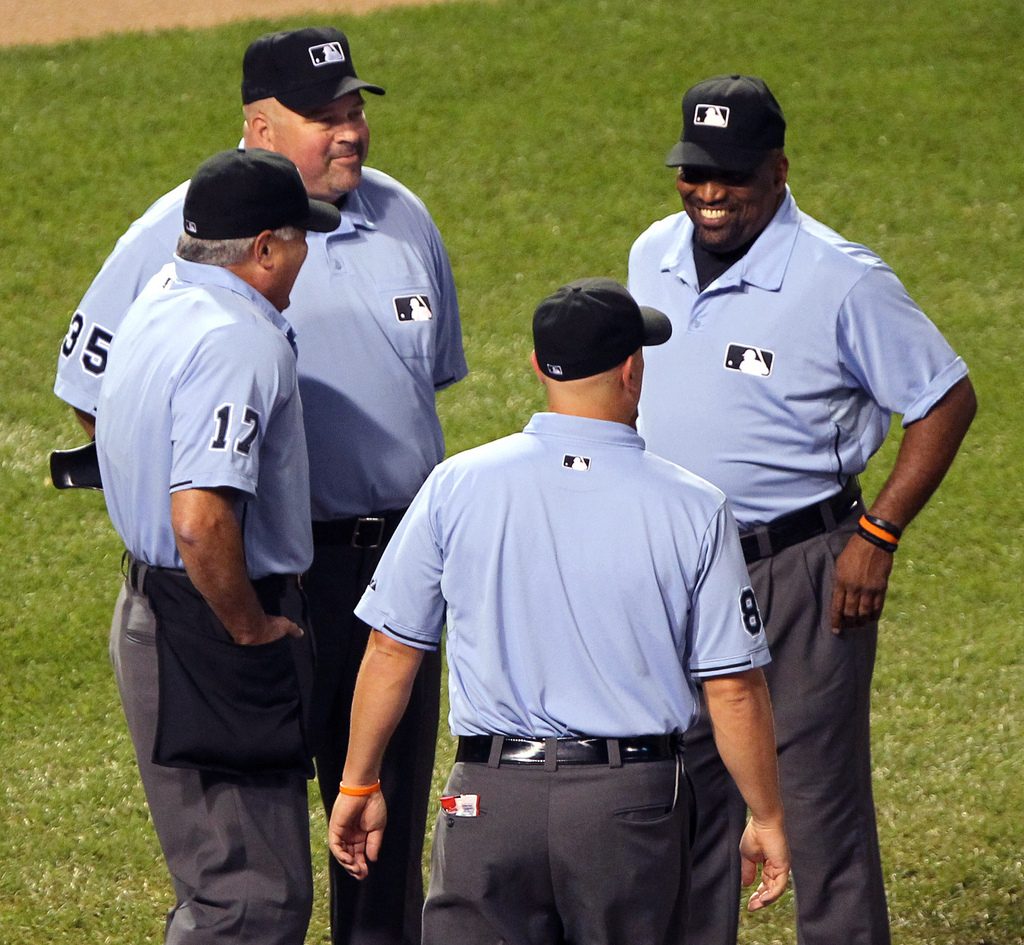
There is some debate about instant replays in baseball. Is the system effective? Close to 50% of replay calls have been overturned in the last few years, so in that regard, mission accomplished. Most of the complaints about replay in baseball have nothing to do with getting the calls right but a whole lot to do with way the system works (more…)
Andre Iguodala, last year’s NBA Finals MVP, throws on a pair of Nike HyperChases, dribbles down a 50 foot court, jumps nearly 35 inches in the air, releasing a basketball at his highest point. A faint swish sound can be heard- Iguodala, the Golden State Warriors guard, has just drained another three point shot. (more…)
With the rise of new healthcare and informatics devices, wearable electronics have seeped into the consumer space and have been quickly adopted by the medical, health, and fitness industries. Industry reports indicate that the market for wearable technology will reach $70 billion by 2025 — $20 billion was spent in wearable tech in 2015 and this is expected to jump to $70 billion by 2025 as the healthcare sector develops more programs and technologies that incorporate wearable tech.
From wristbands with heart rate monitors to calorie trackers and advanced pedometers, many consumers are jumping on the wearable tech bandwagon to keep track of their daily habits and play a more active role in their health. Human resources departments at many major companies and firms have started using wearable tech in the workplace, encouraging employees to take care of their health and wellness so they can be happier, more productive employees. But what types of implications will this have on employees of the future and HR departments at a whole?
Fitbit, one of the leaders in the wearable tech space, announced last year that it will be extending the reach of its corporate wellness programs by making sure its technologies are compliant with HIPAA laws to protect patient privacy. This move allowed the company to give 335,000 Target employees personal fitness trackers and the company already works with more than 50 Fortune 500 companies, according to a report from Fortune Magazine. This means the data Fitbit collects would only be used by certain entities. By extending the reach of their programs, more companies using Fitbit wearable technology would possibly be able to monitor their employees’ health and wellness and possibly have access to employee data.
Companies that have already adopted wearable tech into their company culture are keeping things fairly simple, encouraging employees to pay attention to their health and giving out tracking devices in an effort to support their mission of supporting a healthy workplace. For many companies, like Target, the initiative complements the company’s efforts to promote health and wellness in the workplace.
Of course, this type of access does raise some privacy concerns and questions about whether HR should have this type of information on record — and what they intend to do with it. If companies required all employees to comply and certain employees felt it was too invasive, would these employees have the option to opt out? How much power and authority does the company have when accessing the data they collect? Would they use this information to evaluate an employee’s health status?
These are important questions to consider when exploring the idea of having HR implement any type of wellness program that involves giving employees fitness or health trackers. Some companies have already disclosed that implementing such programs is linked to being able to negotiate lower rates on group insurance policies, according to Bloomberg.
Wearable technologies are here to stay and as more consumers become comfortable with the idea of tracking their daily activities and lifestyle choices, the opportunities for data collection are limitless. However, when HR requires employees to use this technology and share data, there may be some privacy concerns. As long as employees have the option to participate without any repercussions, many companies may be able to adopt wearable tech for the workplace as part of company health and wellness initiatives.
All countries in the European Union (EU) are required to meet certain energy consumption targets each year in an effort to conserve energy and reduce our carbon footprint. Countries all over the world are already experiencing the devastating effects of climate change as we see glaciers shrink, plants and animals dying out early, and rivers and lakes disappearing well before they should. Scientists are already concerned about the effects of global climate change in the near future, assessing the extent of climate change in different environmental systems and ecosystems.
EU Countries Commit to Using More Renewable Energy Sources
Many EU countries are taking the lead on using renewable energy as a primary or secondary source of energy for many industrial and economic activities. According to the European Commission, renewable energy can be produced from several sources. These include wind, solar, hydro, tidal, geothermal and biomass. The goal is to make energy production more sustainable and less dependent on fossil fuels — the longtime fuel source for most companies in the EU.
EU national action plans include renewable energy targets for different sectors, the planned mix of different technologies, any national policies they are developing to better use biomass resources, and measures they are taking to be compliant with EU sustainability criteria. The most important sources in the EU-28 was biomass and renewable waste, according to the latest renewable energy statistics.
How EU Countries Are Taking Steps Towards Sustainability
Thanks to the latest technological innovations and ongoing research studies, EU countries have created renewable energy action plans that outline exactly how they are making use of today’s renewable technologies and meeting their targets in upcoming years. In 2020, for example, each country has committed to reaching national renewable targets — Sweden has committed to having 49% of its energy sources coming from renewable technologies by 2020. Overall, the EU is right on target to meet 2020 goals with total energy consumption projections hovering right around 15% in 2014.
Breaking down the countries who are on track to meet their 2020 targets, we see that Norway committed to 67.5% and was right at 65.5% in 2013. Sweden, Latvia, Finland, Austria and Denmark are extremely close to their targets while Ireland, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Malta and Luxembourg still have some work to do. According to the latest progress reports, only France and the Netherlands failed to meet their 2011/2012 targets — mostly due to lagging energy development initiatives and technical barriers for installing and using sustainable technologies.
One of the most significant changes in the past few years was the creation of the European energy union in 2014. The union was formed to “ensure secure, sustainable, competitive and affordable energy”, according to Eurostat. In 2015, we saw the European Commission move forward with an official climate change policy which included the strategy of decarbonizing the economy.
What Can We Expect from EU Countries in the Future?
Reports reveal China is still the world’s biggest clean energy investor and Asia has been investing heavily in renewables in Europe recently — the first time in 2015, according to Bloomberg. However, investments plummeted last year which has knocked EU countries out of the front lines as a global leader in renewable energy. EU countries still have time to reach their 2020 targets, however, and will continue to work towards cleaning up their sources of energy supply with technological advancements and careful planning.
As the world continues to invest heavily in renewable energy resource development and adopt sustainable practices to fuel the economy in different countries, many countries in the EU are taking the lead on innovation, development and implementation of renewable energy systems. Reducing our carbon footprint and encouraging innovation in the ‘green’ space are high priorities for EU members and today’s efforts will play an important role in our futures, and the future of the our planet.
Innovations in healthcare has shown astounding growth in the past decade from 3D printing of arteries and prosthetics to treatments in diabetes. Though the goal is to do more than just assuage the constant struggle of diabetes sufferers, medical care is heading in the right direction with these 5 new innovations:
Finger Sticks Reduction
One of the complaints heard often from those with diabetes is the pain of finger sticks, and though continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) make it easier to see data, the calibrations have presented problems which can cause a need for more finger sticks.
Abbott’s FreeStyle Flash Glucose Monitoring System intends to answer this concern with its new system that doesn’t need calibration or blood glucose meter. It only uses finger-stick tests for confirmation readings below 70 mg/dl. A small sensor with under the skin filament is held under the arm with adhesive giving a reading of glucose levels minute-by-minute and can read through clothing. The device can store 3 months of data which is useful to track trends.
It has launched in some EU countries and is working on coming Stateside in the near future.
Pump It Up
The modern designed Medtronic’s 640G cuts down on the bulk with its hybrid design. It acts as both a hybrid pump and CGM. The device acts as a pump but monitors the levels to prevent unhealthy limits of insulin. The device is available in Australia and is expected to launch in the U.S. shortly. 
Insulin Reminders
Something as simple as forgetting to take your insulin can lead to not-so-simple problems. Under or over-taking your insulin can be a problem that Timesulin is aiming to wipe out. Timesulin has a timer that starts counting the minute you cap your pen so you’ll be able to see when you took your last dose at a glance on its digital meter. This device works with most pen brands and is already in the U.S.
Breathe Easier
Sanofi and MannKind Corp are in works to offer an alternative to rapid-acting insulin in the form of Afrezza, an insulin powder you use like an asthma inhaler before a meal. The insulin works faster than injected rapid-acting insulin, clears from the body more readily, and cuts down the risk of hypoglycemia. This drug is not intended for smokers, those with asthma, or other lung-related illnesses. Afrezza is already available in the United States for both Type 1 and 2 diabetes.
Skin Deep
In its search to provide a less intrusive method for diabetes to take their medication, Intarcia is looking below skin level. The matchstick-sized device would be implanted below the skin to deliver a constant dose of exenatide for type 2 diabetes which is generally injected twice a day. This device would only need to be injected twice a year significantly cutting down the discomfort of injections. This device plans to clear FDA sometime next year.
These are only 5 of the innovations available or heading our way. There are many more listed at the Diabetes Forecast site. With the trajectory of innovations moving towards alleviating at least some of the problems, the hope is that this momentum will continue and offer even more solutions moving forward.
Renewable energy has been a hot political topic for some years, and the symbolism behind renewable energy has continued to drive political polarization. How dire the issue of renewable energy is subjective to party lines.
On the Democratic side, President Obama promised a move towards renewable energy, since the beginning of his first term has and the proposal of the Clean Power Plan would realize much of his promises. But, this plan has caused a juggernaut of political grandstanding, court battles, and a slew of angry conservatives. The Clean Power Plan would require that states submit their move towards reducing emissions of greenhouse gases to the EPA which has caused a storm of criticism from the right. The EPA advanced with plans to regulate greenhouse gases in power plants and petroleum refineries in 2011 and saw the House Republicans going on the offensive to block the move. And conservative states continue to fight.
According to Robert Walton’s Utilities Drive newsletter, 24 States (mostly the Red States) filed lawsuits against the EPA to block the bill:
<blockquote>In total, states opposed to the rule include: Alabama, Arizona, Arkansas, Colorado, Florida, Georgia, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, New Jersey, North Carolina, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Ohio, South Carolina, South Dakota, Texas, Utah, West Virginia, Wisconsin and Wyoming. </blockquote>
This turnout against the bill is relevant because the number of states involved in the melee is unheard of said Joe Stanko, an attorney at Hunton & Williams, “I can’t recall a Clean Air Act rule, or other EPA rule, that has 44 states in the mix.”
Interestingly, more than 10 years ago, President George W. Bush signed the Energy Policy Act of 2005energy bill that was supported by then Senator Obama (D-III) to the chagrin of environmentalists. The bill was the first since the mid-70s that addressed fuel-efficiency regulations in automobiles by 40 percent – with a blending of ethanol in the U.S. fuel supply by 2022. The federal tax credits initially credited solar usage, but the Extension Act of 2008 extended the credit to wind energy and geothermal heat. Subsequent provisions included gave an extension credit for another eight years (which runs out at the end of 2016).
With the credits to expire in December of this year, though a commercial 10% will continue, the reps at the House may kill any further extensions. However, not all conservatives are taking affront to this pro-renewable move. The Tea Party has made unusual bedfellows with environmental groups. Debbie Dooley, the national coordinator for Tea Party Patriots and co-founder of the Green Party Coalition has come out against conservatives’ pushback towards renewable. Said Dooley of Georgia, “They [conservatives] neglect to mention billions of dollars that the fossil-fuel industries have received,” she said. “They cherry-pick their principles.”
Tom Morrissey, former Arizona state Republican Party chairman calls the Tea Party leaders “knuckleheads” for their stance on the issue saying it is a national security issue. “If we can keep one dollar from going to people who are killing our kids in Afghanistan, it’s a good thing — and I feel that’s what solar energy does.”
Regardless of the out-fighting or in-fighting, truth is that solar power is the fastest growing and most divisive source of energy and will no doubt bare its head come next election.
Whether for home solar panels or electric vehicles, it’s common for governments to offer consumers subsidies for buying and using sustainable products. Unfortunately, it’s an imperfect process: given the uncertainty of market demands, it’s difficult to project numbers that correlate accurately with sales.
Why settle for inaccurate, ineffective subsidies? Shouldn’t there be a better way to calculate them? The short answer is yes, and a new paper by MIT researchers sought to find out how. The paper shows that governments are likely to make subsidies too low due to market uncertainty, and ways in which it can be improved. Their intention was to design a better way to back clean technology.
The paper, co-authored by doctors and professors Georgia Perakis, Maxime C. Cohen, and Ruben Lobel, is called “The Impact of Demand Uncertainty on Consumer Subsidies for Green Technology Adoption.” It was published online by Management Science.
Governments typically provide subsidies based on overall adoption targets: the number of products they’d like to see adopted over a period of time, rather than a realistic projection. Since cleantech products are usually new, it’s hard to know whether the demand will be huge or non-existent without a crystal ball.
Higher subsidies?
To figure out better model for subsidies, the project examined existing products and their subsidy levels to determine whether the subsidy was effective. They concluded that in most cases, the subsidy should have been as much as five times higher to kickstart sales.
Higher subsidies, the authors say, is critical for cleantech product launches because it helps sell products faster and at a higher volume. These increased subsidies should pay for themselves, they say, because of the estimated savings in the larger context by preventing environmental damage and the costs associated.
The paper found that higher subsidies would drive the adoption of green technologies in their early stages, spurring their growth. As sales grow, the subsidy level could be adjusted accordingly.
The research has been called “important and timely” by experts, but not all are on the side of subsidies for innovation. Subsidies, the contrarians say, can put undue strain on government finances and are unable to respond to market changes, which can lose investors money. Still, I remain optimistic about overall adoption of new clean technologies: if there is value in subsidies for the earth and for consumers, and accuracy is prioritized, it’s a win-win scenario.
Featured image: Tony Hall via Flickr
True crime stories make for fantastic entertainment, but as Netflix docu-series Making a Murderer has proven, they are much more than popcorn fodder. As eye-opening illustrations of real-life legal proceedings, airing these cases can expose all-too-common injustices in America’s justice system.
Dream / Killer, released in 2015, is a documentary detailing how an innocent man was sentenced and imprisoned for a crime based on someone else’s dream. The film, which debuted at the 2015 Tribeca Film Festival, details the 9-year journey of Bill Ferguson’s attempt to free his son from a 40-year murder sentence.
Two years after the 2001 strangling of sports editor Kent Heitholt, Ryan Ferguson was implicated in the murder by his friend Chuck Erikson, who dreamt their involvement and later confessed to it. The film utilizes real footage from Kevin’s arrest, prison interviews and court hearings to shine light on the inner-working of shaky legal proceedings. The footage reveals that together, police coercion and prosecutorial misconduct work to fabricate and push a narrative of a crime with little basis in reality. Their influence put the two men in prison for murder and robbery.
The good news is this: in 2013, Ferguson’s conviction was overturned on the basis that the prosecution withheld evidence from the defense. Indeed, under-oath testimony from a witness that said she did not see Ferguson on the scene was omitted, along with that of a witness that saw the men leave the bar at a time that didn’t match the prosecution’s story. Kathleen Zellner, the defense lawyer currently representing Making a Murderer’s Steven Avery, was a key player in Ryan’s exoneration.
Erickson, who took a plea deal of 25 years for implicating Ferguson despite his lack of memory, remains in prison to this day.
Above all else, Dream / Killer is a story of father and son perseverance and an extraordinary dedication to justice in the face of legal misconduct. The Fergusons agreed to do the film for awareness purposes. “We realized that we were in a position to show the world what could happen to them,” Ryan told the Innocence Project of the documentary. “This could happen to my father and any other of our friends and family, and that’s really scary.”
Ryan’s father Bill added that the general public should be aware of what’s called a Brady Violation, which happens when prosecution suppresses evidence favorable to the defence. “…if the public’s aware of it, and the prosecutors are aware that the public knows about it, I think we’ll see less abuse,” Bill said. “By us exposing this, and raising awareness, we can hopefully help bring about some changes.”
In a former blog post, I detailed some other recommendations beyond awareness that might keep law enforcers accountable for these types of errors, and hopefully prevent false convictions in future cases. While documentaries like Dream / Killer are great for exposure, it takes real policy changes to stop their root causes.
When the largest game of the year is hosted in California’s Bay Area, you can expect the NFL to get a little help from the locals: Silicon Valley tech giants. This year’s game, as the 50th Super Bowl, was an important anniversary worthy of showcasing the latest specs in technology. From the stadium, to the halftime performance, to the athletic gear, #SuperBowl50 did not hold back.
As it happened, the game itself wasn’t much to brag about. The Denver Broncos beat the Carolina Panthers 24 to 10 in a monotonous display of good defense, which though a feat for Peyton Manning did not make for exciting viewership. Luckily, there’s so much more to the Super Bowl these days than touchdowns and field goals. What lacks in the match can be made up for by the digital fan experience, both onscreen and behind the scenes. This year, boundaries were broken in both the delivery and the message of technology at its finest.
The support
The spectrum of Super Bowl 50’s technology didn’t begin and end on February 7th in San Francisco. Rather, it was many months in the making, with preparation taking up a huge portion of technological real estate, so to speak.
The Super Bowl Host Committee is largely responsible for ensuring these preparations come together smoothly in the weeks leading up to the game. This year, the committee’s CEO Keith Bruce emphasized that first and foremost, Super Bowl 50 would be all the about the tech.
“Our goal was to be the most technologically advanced Super Bowl ever,” Bruce said. “We’re at the center of the digital economy of the world, home to a lot of the stalwarts of tech, and we thought we should embrace that.”
Software and tech companies needed very little urging to get on board with this mission. Transportation came via Google’s commuter fleet and Uber on-demand, while laptops, phones and other equipment were provided by Apple. Google also helped develop the Road to 50 app, a virtual guidebook to the event, which fans could use to order food to their seats enjoy other perks.
With the help of Verizon and other providers, Levi’s stadium fully equipped with 400 miles of fiber optic cable, 1,200 wifi access points and 1,700 BlueTooth beacons to keep fans connected at all times. All in all, the committee raised $50 million from corporate sponsors to hold Super Bowl 50 to the highest of standards, worthy the sport’s 50 year mark and the region’s technology prowess.
The specs
Beyond sponsorships, the fun continues from all angles. Super Bowl 50 featured camera technology was at its finest: the EyeVision 360 displayed a 360 view of the stadium streamed from 36 cameras around the venue, while the debut of the Pylon Cam placed 16 cameras in end zones to film goal line sand sidelines, aiding officials in making tough calls. Athletic gear has advanced over the years as well — this year, players donned state of the art gear with RFID tracking in their shoulder pads.
Behind the scenes, there’s also advanced cyber security to take into account. Following terror attacks in Paris and San Bernardino, the biggest American sporting event of the year took no chances with security — luckily, and they had the technology available to make it an utmost priority. Though FBI declined to reveal their measures in full detail, we do know that disarming robots, helicopters, military jets were on standby.
Perhaps the greatest security measure, though, was surveillance. With over 600 cameras and an advanced scanning system that aggregated threats from the ground, sky, and social media, streams of real-time data were analyzed by agents at a Joint Operations center at an undisclosed location.
The social
Social networking continues to be an enormous boon for brands and fans alike. The “second screen” experience, which allows live tweets and commentary from anyone with a device, proved successful once more: it’s is the ultimate augmentation of the Super Bowl, maximizing engagement in and out of the stadium.
Since the game wasn’t stirring up huge excitement in and of itself, we can thank our lucky stars for the halftime performance, which generated significant buzz online. Halftime shows often feature high-tech spectacles: for example, the mechanical cat ridden by Katy Perry last year, which was somehow overshadowed by the antics of Left Shark.
This year, Coldplay lead a technicolor display complete with interactive light-up LED wristbands, video walls, lasers and light-up inflatable balls. But as if proving technology for technology’s sake is bound to fall flat, it was Beyonce that stole the show with the performance of her brand-new song “Formation.” Together, Beyonce, Chris Martin and Bruno Mars evoked themes ranging from LGBT pride to African American empowerment, making the show as politically charged as it was electronically.
All in all, fans of the Broncos, Beyonce, and technology should be pleased with Super Bowl 50. And for those still unsatisfied, there are only seven more months until football season starts up again, with the power of a million screens and screams close behind.
Featured image: duluoz cats via Flickr
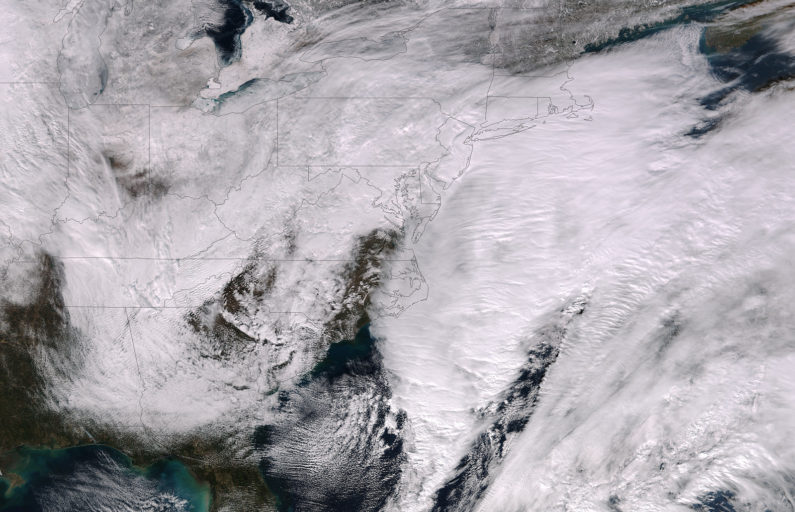
In the aftermath of a winter storm that mercilessly slammed DC to NYC this past weekend, severe weather is on the minds and lawns of many Americans this winter. Mother nature can be an unforgiving force in all regions and seasons: whether she manifests as a sizzling drought or blizzard of the ages, humans are left to scramble for safety with emergency supplies and stockpiles of canned goods. Too often, severe weather events lead to injuries, deaths, and costly damages to property and infrastructure.
Living on a planet with a weather cycle and plate tectonics comes with its inherent risks, and that’s not to mention the severe weather events that climate instability could result in. Regardless of cause, humanity is lucky in the sense that we’re better able to predict, prepare, and stay safe under dangerous conditions. This is largely due to the advancement of weather, disaster relief, and rescue technology.
Extreme weather and other natural disasters can now be detected early on, meaning you’re unlikely to have a typhoon sneak up on you reading Kafka on the beach. It’s thanks to technology that this early and accurate forecasting is possible: for decades, doppler radar, observation tools and computer calculations have been utilized to generate weather predictions. The improvement of these tools along with the addition of weather satellites has upped the accuracy of forecasting over time.
The improvement of forecast technology has been instrumental in the implementation of weather alerts and other types of notifications that help people prepare for harsh weather. Tools like the American Red Cross’ DigiDoc send mass alerts to people in affected areas; most of smartphone owners in the US have built-in alerts that warn of flash floods and other weather-related dangers. Sometimes these may seem superfluous — if it’s raining hard, you probably don’t need a text to tell you — but if the weather event is something like a tornado, these alerts can save lives.
There’s also new technology that allows people to stay connected and safe both during and after severe weather events. Facebook recently released a tool called “Safety Check” that lets people in disaster-affected areas check-in to let their friends know they are safe. But technology goes beyond even this — survivors can alert emergency responders with their mobile phones, sometimes even without Internet connection, for example, through mesh networks like the Serval Project. There are also many emergency and survival apps that work with or without wifi and cell service.
For those in need of emergency relief, rescue and assistance has improved tremendously over the years as well. From drone supply deliveries to rescue robots and radar search tools, individuals at risk can be located, supplied, and ultimately rescued from unsafe areas — whether from flooded homes or piles of rubble.
It’s a relief to know that through the blizzards of today and the quakes of tomorrow, the probability of safety and survival is greater thanks to intelligent minds and effective technology. While we’ve no way yet to change or control the weather all together, the ability to detect danger and avoid harm is a bright spot in a stormy sky, capable of saving millions of lives (and dollars) each year.
Featured Image: NASA GSFC via Flickr.